Chemical and bioprotective studies of Xylopia aethiopica seed extract and molecular docking of doconexent and cryptopinone as the prominent compounds
Keywords:
Xylopia aethiopica, Phytochemicals, Antioxidants, Antibacterials, Molecular dockingAbstract
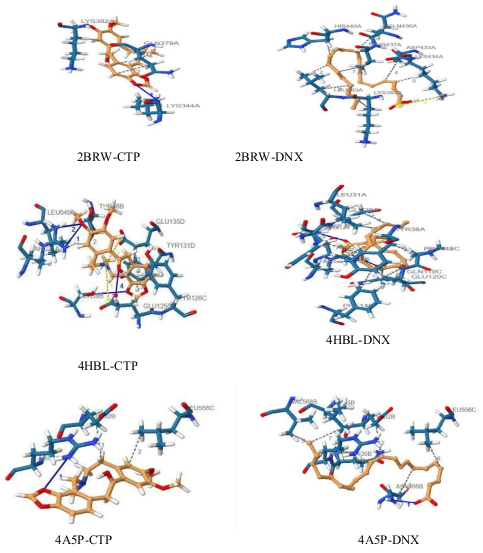
Fourteen phytochemical compounds were identified in the gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) analysis of the petroleum ether extract of the seeds of Xylopia aethiopica. The compounds comprised of terpenoids (56.027 %), unsaturated fatty acids (30.081 %), alcohol (9.385 %) and saturated fatty acid (4.507 %). The extract showed high antioxidant activity in a dose dependent pattern at a minimum and maximum concentrations of 25 and 400 μg/ml respectively and could be compared with that of ascorbic acid used as a standard antioxidant agent. The antibacterial activity screening of the extract against five pathogenic bacteria organisms indicated that the extract possessed more antibacterial activity than gentamicin used as a standard antibacterial agent. The trend of activity was Klebsiella pneumoniae (gram-negative) > Shigella flexneri (gram-negative) > Staphylococcus epidermidis (gram-positive) > Escherichia coli (gram-negative) > Streptococcus pneumoniae (gram-positive). The presence of high amount of terpenoids in the extract of X. aethiopica could be the reason for the high antioxidant and antibacterial activities shown by the extract and also suggests why the seed extract of the plant is used in herbal medicine for the treatment of diseases and infections. All of the test compounds had negative binding affinities, according to molecular docking modelling, indicating that the compounds had been successfully docked to the receptors. The compounds showed good pharmacokinetic properties, such as high blood-brain barrier absorption, oral bioavailability, and water solubility, in the in-silico ADME and drug-likeness predictions. The findings of this study significantly increase the relevance of these compounds as promising first targets for the treatment of drug resistant bacteria. This may help pharmacologists and other medicinal chemists create and synthesize even more potent drug candidates.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 O. U. Igwe, C. C. Oru, I. E. Otuokere

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Ifeanyi Edozie Otuokere, Onyinye Uloma Akoh, Felix Chigozie Nwadire, Chinedum Ifeanyi Nwankwo, Joy Nwachukwu Egbucha, Chiemela Wisdom, Ogbonna Augustine Okwudiri, GC-MS Profiling and In Silico Studies to Identify Potential SARS-CoV-2 Nonstructural Protein Inhibitors from Psidium guajava , African Scientific Reports: Volume 1, Issue 3, December 2022
- Hassan Ibrahim, Deborah Abolape Akwu, Reza Sharafdini, On topological indices and QSPR analysis of some drugs used for treating Coronavirus patients , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 2, August 2024
- Tosan Peter Omayone, Ibrahim Aliyu, Grace Iyabo Adebayo-Gege, Impact of high protein diet on the formation and healing of L-arginine induced acute pancreatitis in male wistar rats , African Scientific Reports: Volume 4, Issue 1, April 2025
- Oluwagbenga Anifowose, Bitrus W. Tukura, Obaje D. Opaluwa, Detoxification of Ochratoxin A in Rice and Maize using ethanolic leaf extracts of Moringa oleifera and Vernonia amygdalina , African Scientific Reports: Volume 4, Issue 2, August 2025
- Isaiah Eze Igwe, Yusuf Tajuddeen Batsari, Atomistic Simulation of the Effect of Temperature on Mechanical Properties of some Nano-Crystalline Metals , African Scientific Reports: Volume 1, Issue 2, August 2022
- Grace Adebayo-Gege, James Adiwu, Abednego Ovey Angbashim, Toyin Dorcas Alabi, Murtala Ngabea Audu , Frank Abimbola Ogundolie, Attenuation of indomethacin-induced gastric ulceration by methanolic extract of Cucumis Melo (L. indorous) seeds in male Wistar rats , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 3, December 2024
- Matthew Olaleke Aremu, Stephen Olaide Aremu, Ibrahim Aliyu, David Bala Passali, Munir Hussaini, Benjamin Zobada Musa, Rasaq Bolakale Salau, Amino acids profile and health attributes of Bambara groundnut (Vigna subteranea L.) and sesame (Sesamum indicum L.): a comparative study , African Scientific Reports: Volume 4, Issue 1, April 2025
- C. E. Achikanu, I. I. Ujah, O. N. Ani, C. A. Nsude, K. O. Okolo, D. O. Okeke, C. U. Ekekezie, V. E. Okpashi, L. C. Okwesili, I. O. Okpako, E. O. Nneji, C. A. Anieke, Environmental degradation of Nike lake: a study on water quality parameters and heavy metal accumulation in fish , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 3, December 2024
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Ifeanyi Edozie Otuokere, Onyinye Uloma Akoh, Felix Chigozie Nwadire, Chinedum Ifeanyi Nwankwo, Joy Nwachukwu Egbucha, Chiemela Wisdom, Ogbonna Augustine Okwudiri, GC-MS Profiling and In Silico Studies to Identify Potential SARS-CoV-2 Nonstructural Protein Inhibitors from Psidium guajava , African Scientific Reports: Volume 1, Issue 3, December 2022
- Ezenwa Kelvin Iheanacho, Okenwa Uchenna Igwe, Princewill Ezenwa Ndubueze Onyemachi, GC-MS analysis and hypoglycemic properties of methanolic leaf extract of Cnidoscolus aconitifolius onalloxan-induced diabetic Wistar rats , African Scientific Reports: Volume 2, Issue 3, December 2023



