Impact of high protein diet on the formation and healing of L-arginine induced acute pancreatitis in male wistar rats
Keywords:
High protein diet, L-arginine, Acute pancreatitis, Antioxidants, MDAAbstract
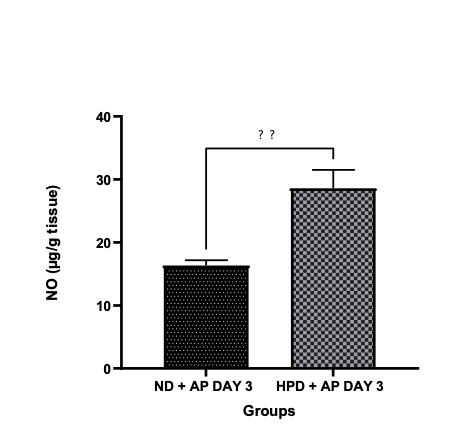
The condition known as acute pancreatitis is defined as the inflammation of the pancreas, commonly caused by gallstones and alcohol ingestion. The paucity of information on its management in combination with other factors such as adverse effects resulting from treatment has redirected the attention of researchers to safer, alternate therapies. This study aims to assess the role of a high-protein diet in mitigating acute pancreatitis caused by L-arginine. Two groups of twenty male rats were randomly assigned; groups fed with normal diet (NP), and groups fed with high-protein diet (HPD). Acute pancreatitis was induced with L-arginine monohydrochloride at dose of 250mg/Kg. It was administered 3 times at interval of one hour. After induction, the groups were further grouped into subgroups upon observations on day 3 and day 7. Lipid peroxidation (MDA level), total protein and antioxidants parameters such as hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide. sulfurhydric acid concentration, total antioxidant capacity (TAC), CAT, GPx and NO were evaluated using spectrophotometry. Every data set was shown as mean °æ SEM and as an ANOVA with a post-hoc analysis at α= 0.05. Findings revealed that the high protein diet administered significantly increased the protein level, sulfurhydryl concentration, TAC, CAT, GPx and NO compared to the acute pancreatitis model on day 3, and had no significant effect in most parameters on day 7. Lipid peroxidation substantially decreased in the treatment groups when compared to pancreatitis model. High protein diet improves the amelioration of acute pancreatitis by enhancing the antioxidant enzymes, nitric oxide and inhibiting the process of lipid peroxidation.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Tosan Peter Omayone, Ibrahim Aliyu, Grace Iyabo Adebayo-Gege

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Matthew Olaleke Aremu, Stephen Olaide Aremu, Ibrahim Aliyu, David Bala Passali, Munir Hussaini, Benjamin Zobada Musa, Rasaq Bolakale Salau, Amino acids profile and health attributes of Bambara groundnut (Vigna subteranea L.) and sesame (Sesamum indicum L.): a comparative study , African Scientific Reports: Volume 4, Issue 1, April 2025



