Environmental degradation of Nike lake: a study on water quality parameters and heavy metal accumulation in fish
Keywords:
Pollution, Heavy metals, Nike lake, Clarias gariepinus, Tilapia zilliiAbstract
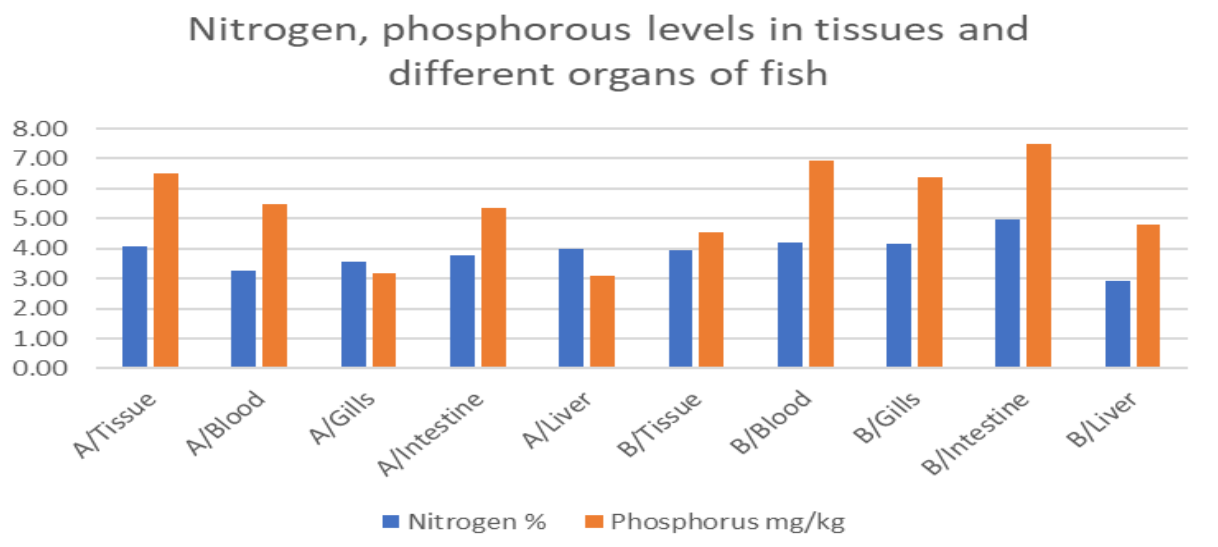
Environmental pollution is a pressing global issue, with heavy metal pollution posing a significant threat. This study examined the concentrations of heavy metals (cadmium, nickel, lead, chromium, manganese, iron, zinc, copper, mercury, selenium, and arsenic) in various organs and tissues (blood, gills, intestines, liver) of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) and Redbelly Tilapia (Tilapia zillii) from Nike Lake in Enugu State, Nigeria. Water samples from the lake were also analyzed for heavy metal concentrations, as well as nitrogen and phosphorous content, nitrate, phosphate, and dissolved oxygen levels. The results showed that the fish samples contained varying concentrations of heavy metals, with the highest levels found in the gills. The ranges of metal concentrations were: Cd (0.00-0.033), Ni (0.00-0.002), Pb (0.00-0.072), Cr (0.00-0.039), Mn (0.00-0.041), Fe (0.010-1.363), Zn (0.268-0.604), Cu (0.008-0.084), Hg (0.00-0.147), Se (0.293-0.474), Mo (0.020-0.095), and As (0.00-0.034). The water samples contained similar concentrations of heavy metals, were Cd:0.02, Ni:0.001, Pb:0.034, Cr:0.00, Mn:0.012, Fe:0.037, Zn:0.173, Cu:0.008, Hg:0.147, Se:0.309, Mo:0.027, As:0.004, with the addition of nitrate (4.373), phosphate (4.383), and dissolved oxygen (45.33) levels. The nitrogen and phosphorous content in the fish organs ranged from 2.938-4.987 and 3.089-7.484, respectively. The study highlights the presence of toxic heavy metals in the organs of the fish, emphasizing the need for regulation and monitoring to mitigate the risks associated with heavy metal pollution in aquatic ecosystems.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 C. E. Achikanu, I. I. Ujah, O. N. Ani, C. A. Nsude, K. O. Okolo, D. O. Okeke, C. U. Ekekezie, V. E. Okpashi, L. C. Okwesili, I. O. Okpako, E. O. Nneji, C. A. Anieke

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



