Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction/HPLC techniques for determination of oxytetracycline and doxycycline residues in beef samples: method developments and statistical analysis
Keywords:
beef, liquid chromatography, microextraction, tetracyclines, validation`Abstract
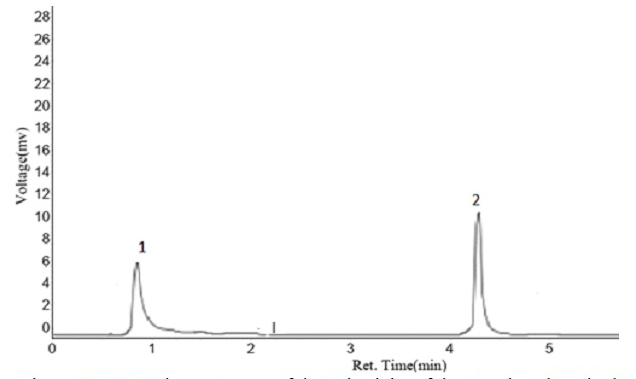
A rapid, cost-effective and environment-friendly sample pre-treatment method involving dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was developed and applied for the extraction of oxytetracycline and doxycycline residues in beef samples (liver, kidney and muscle). Several influencing factors associated with the extraction and separation of these antibiotics residues, such as sample size, type and volume of disperser and extraction solvents, centrifugation speed and time, were optimized using Plackett-Burman design and central composite design, while insignificant factors were fixed at values determined using univariate analysis. Figures of merit of the analytical methodology including the limit of detection (LOD), the limit of quantification (LOQ), accuracy (in terms of average recoveries), precision and calibration functions were established according to the European Union commission decision 2002/657/EC. Linearity, in the range of 5–500 µg/kg, was obtained with regression coefficients ranging from 0.9983 – 0.9999. Inter-day repeatability, intra-day precision, LODs and LOQs obtained were 3.81 – 14.90%, 3.80 – 8.70%, 4.21 – 4.69 µg/kg and 14.02 – 15.65 µg/kg respectively. Samples with detectable drug residues have oxytetracycline being the most commonly detected. The developed method was successfully established and the concentration levels of drug residues detected were lower than the European Union set maximum residue level (MRL).
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 M. A. Aliu, A. M. Junaid, A. Ibraheem, A. Ishaq, A. Lawal, K. E. Ayeni, A. R. Lawal, L. B. Abdulrauf

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Oluwagbenga Anifowose, Bitrus W. Tukura, Obaje D. Opaluwa, Detoxification of Ochratoxin A in Rice and Maize using ethanolic leaf extracts of Moringa oleifera and Vernonia amygdalina , African Scientific Reports: Volume 4, Issue 2, August 2025
- Eno Chongs Mantu, Olukayode Olugbenga Orole, Aleruchi Chuku, Femi Gbadeyan, Tosin Okunade, Assessment of mycotoxin presence and distribution in maize grains across North central states of Nigeria , African Scientific Reports: Volume 4, Issue 3, December 2025
- Gabriel James, Anietie Ekong, Etimbuk Abraham, Enobong Oduobuk, Nseobong Michael, Victor Ufford, Oscar Ebong, An enhanced control solutions for efficient urban waste management using deep learning algorithms , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 3, December 2024
- Saheed Adekunle Ganiyu, Oluwaseun Tolutope Olurin, Sulaimon Yinka Makanjuola, Anthony Okeh, Abiodun Oluwatoyin Salawu, Rasaq Akanji Lasisi, Assessing the physical and geotechnical properties of subsoils within an active municipal solid waste dumpsite for secured future urban growth , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 2, August 2024
- O. U. Igwe, C. C. Oru, I. E. Otuokere, Chemical and bioprotective studies of Xylopia aethiopica seed extract and molecular docking of doconexent and cryptopinone as the prominent compounds , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 2, August 2024
- Ahmad M. Shuaibu, Kizito O. Musa, Ijioma M. Okiyi, Groundwater recharge modelling using SWAT analysis for groundwater reserve quantification of Ka watershed catchment area part of Sokoto-Rima Basin, North West Nigeria , African Scientific Reports: Volume 4, Issue 1, April 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.



