Effect of viscosity on reservoir deliverability of greenfield, Niger-Delta, Nigeria
Keywords:
Deliverability, Terminal Velocity, Viscosity, Injection, ReservoirAbstract
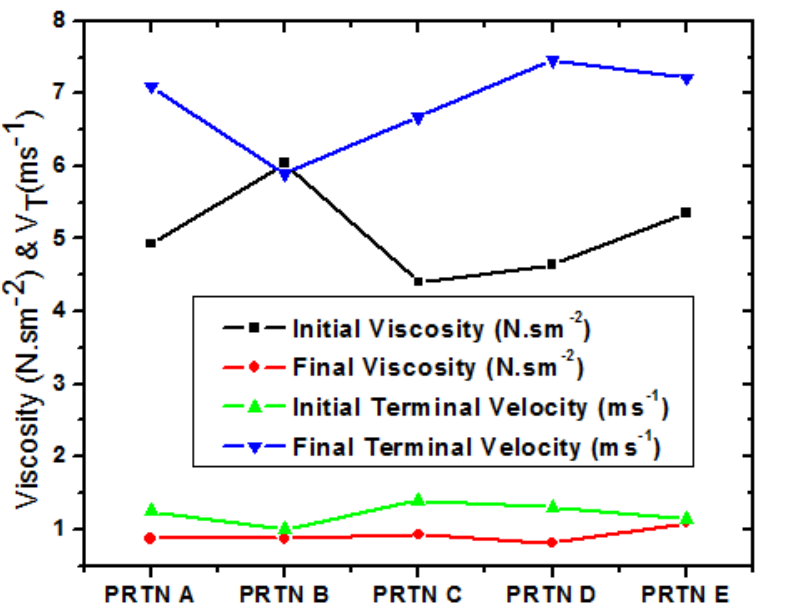
Reservoir deliverability has been a concern in exploration geosciences as it determines the volume of hydrocarbon that is exploitable from a reservoir. In this research, we recorded the viscosity (η) of fluid from Green field in order for us to have an idea of its deliverability. Different quantity of heat was injected in the form of steam into Green reservoir fluids at every 30 minutes interval and the changes in the viscosity at every considered temperature were estimated to determine the reservoir deliverability. Reservoir fluid from Green field were collected every 30 minutes interval to obtain its terminal velocity (VT ) which is needed to estimate η. The viscosity and deliverability of the reservoir in percentage were 5.073 Nsm-2 and 40% before the injection of steam. Each of the 30 minutes interval of temperature increase after the injection of steam showed a direct variation of the temperature with VT and an indirect variation with η of the fluids. Each of the reservoir fluids collected for five different times from Green field were divided into five portions. After steam injection, the first, second, third, fourth and the fifth collected fluids, respectively, produced an average VT and η of 2.83 ms-1 and 2.164 Nsm-2 , 3.89 ms-1 and 1.576 Nsm-2 , 4.82 ms-1 and 1.272 Nsm-2 , 5.92 ms-1 and 1.034 Nsm-2 and 7.07 ms-1 and 0.865 Nsm-2 which depicts easy movement of hydrocarbon as temperature increases. The percentage average deliverability of the reservoir after the application of heat at five different 30 minutes interval temperature change becomes 53.44% which showed clearly that for non-volatile hydrocarbon, reservoir deliverability can be improved upon by injecting heat as it reduces viscosity and enhances easy mobility of hydrocarbon up the wells.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 D. S. Adepehin, L. C. Anu, A. B. Babinisi, A. I. Odudu, T. A. Olajide, D. D. Awosika, A. Ikusika

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Surajo Muhammed Gwio, Ibrahim Ayuba, Umar Faruk Aminua, Development of 3D flow diagnostic numerical simulator and rock property modelling for a homogeneous faulted reservoir , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 1, April 2024
- Surajo Muhammed Gwio, Ousmane Soumah, Comparative analysis of pure CO2 and CO2 enhanced polymer flooding: a numerical modelling approach , African Scientific Reports: Volume 4, Issue 1, April 2025
- Ahmed Mahi Shuaibu, Bathymetric survey and volumetric analysis of Bakolori dam reservoir North West Nigeria , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 2, August 2024
- Shadreck Muyambo, Jack A. Urombo, Temperature-dependent viscometry of baobab pectin (Adansonia digitata L.) , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 1, April 2024
- K. W. Bunonyo, E. Amos, Convective Flow of Blood through a Constricted Cylinder and the Effect of Cholesterol Growth Rate on the Motion in the Presence of a Magnetic Field , African Scientific Reports: Volume 1, Issue 3, December 2022
- Solomon Denen Igba, Idugba Mathias Echi, Emmanuel Vezua Tikyaa, Simulation of thermochemical effects on unsteady magneto hydrodynamics fluids flow in two dimensional nonlinear permeable media , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 3, December 2024
- I. D. Dorothy, I. M. Echi, A. N. Amah, Numerical simulation of a nonlinear diffusion type equation in a two phase media with linear porosity and permeability model , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 1, April 2024
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.



