Biogas Production: A Comparative Study of Chicken Droppings (Poultry Waste) and Banana Peels as the Gas Source
Keywords:
Bioproduct, Bio-waste, Syngas, Bioenergy harvestAbstract
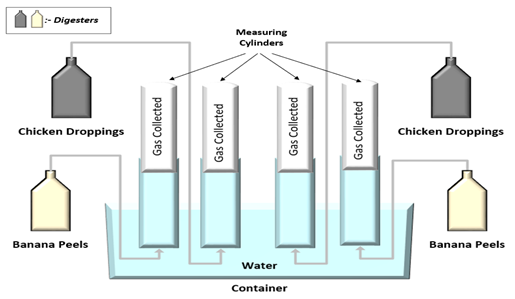
Biogas has been increasingly used in generating energy in the deregulated energy market. Biogas production has been identified as a sustainable approach to mitigating the effect of climate change and global warming. This work conducted a comparative study of biogas production from poultry waste (Chicken droppings) and banana peels under the same operating conditions. 100g of each sample was mixed with 200cm³ of water for poultry waste and 400cm³ for banana peels and loaded into four cylindrical digesters. Each container was shaken to ensure a homogenous mixture and fermentation. Biogas was measured using the water displacement method for 14 days at an average of 27.7oC. The pH, temperature, and concentration were observed to affect biogas production. Within 14 days, 1556cm3 and 755cm3 of biogas were produced for poultry waste and banana peels. This shows that poultry waste produces more biogas than banana peels. Hence, it can be deduced that poultry waste is potentially a more promising feedstock for biogas production than banana peels; and can provide an alternative energy source for the local community in place of the conventional fossil fuel source.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 Abdullahi Usman, Tijjani Ali, Khalifa Aliyu Ibrahim, Magaji Ismail

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



