Efficient and optimal adsorptive removal of urea from agricultural effluent using acidified ball clay: optimization via response surface methodology
Keywords:
Acid modified, Ball clay, Characterization, Contamination, RemediationAbstract
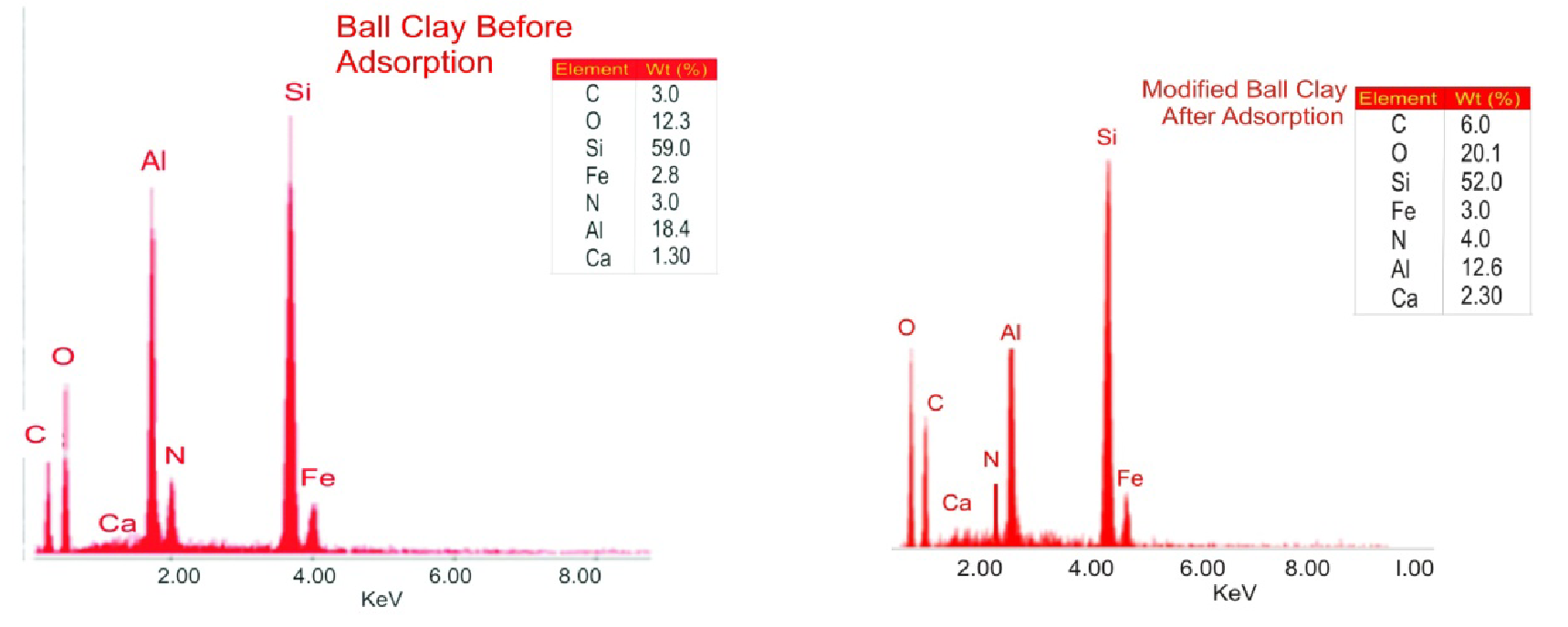
Agricultural runoff rich in urea content poses a threat to the aquatic ecosystems. This study investigated the adsorptive potential of acidified ball clay in removing urea from agricultural effluents as well as the conditions of temperature, adsorbent dosage, time, and pH that will give the optimum removal by adopting response surface methodology (RSM). Characterizations of the acidified ball to understand its adsorptive properties revealed the abundance of visible pores on the acidified ball clay for possible accommodation of adsorbate (urea) by SEM, while after adsorption the initial visible pores are slightly batched, indicating interaction between the adsorbate and adsorbent. The TEM analysis showed a number of spherical-shaped and well-dispersed nanostructures of adsorbent whose number doubles on addition of adsorbate after adsorption. The FTIR spectrum of modified ball clay showed the presence of O-H, Si-O-Si, and Al-OH groups. The EDX spectrum for the acidified ball clay unveils the elemental composition by weight in the order: Si (59.0%) > Al (18.4%) > O (12.3%) > N (3.0%) = C (3.0%) > Fe (2.8%) > Ca (1.3%). The batch process showed that acidified ball clay exhibited good potential for urea adsorption. Achieving a maximum removal efficiency of 89.14% with a corresponding capacity of 1815.3 mg/g from an initial concentration of 152.7 mg/L at optimum conditions of pH =3, temperature = 35°C, dosage 3.75 g, contact time = 30 minutes, and rate of 4.53 min-1.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2026 E. A. Yerima, S. P. Maaji, C. V. Ogbodo, D. Abutu, S. A. Yakubu, F. O. Nwankwo, S. J. Aboki, J. A. Adamu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- E. A. Kamba, E. A. Yerima, Gas-phase Photocatalytic Oxidation of 1-Hexene Using Heterogeneous Semiconductor Materials , African Scientific Reports: Volume 2, Issue 1, April 2023
- E. A. Yerima, A. U. Itodo, R. Sha’Atob, R. A. Wuana, G. O. Egah, S. P. Ma’ajia, Phytoremediation and Bioconcentration of Mineral and Heavy metals in Zea mays Inter-planted with Striga hermonthica in Soils from Mechanic Village Wukari , African Scientific Reports: Volume 1, Issue 2, August 2022



