Shielding Adequacy of Conventional X-ray Facilities in Kano Metropolis, Nigeria using RadShield Software
Keywords:
Shielding, X-ray, RadShielding, BarrierAbstract
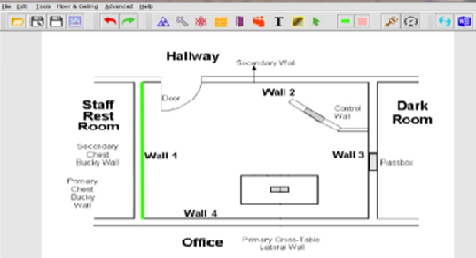
Over time x-ray department gains more patient throughput compared to when it was established, this may lead to changes in room usage, workload and occupancy factor. Therefore, it becomes imperative to re-evaluate the shielding adequacy of the facilities to ensure the appropriate shielding design goal is accomplished. The study was aimed at assessing the shielding adequacy of conventional x-ray rooms in ten radio diagnostic centres in Kano Metropolis using RADSHIELD software. This was a prospective, cross-sectional study. RadShield software version 1.1 was used in the study, parameters such as distances of each wall from a radiation source (D), the average number of patients per week (N), occupancy factor (T), and use factor (U) were inserted into the software together with the shielding design goal (P). Once the result was generated, the design and shielding variables were saved in .xml format. The data were analyzed using Excel 2016. Ten facilities were studied involving 14 x-ray rooms. Room III had the largest room size of 49.2 m2 while room X had the least room size of 12.8 m2. Room II had the longest source image distance (SOD) of 180cm while room IV had the shortest (120cm). The design barrier thickness was thickest (47 cm) in room II and thinnest (1.5 cm) in barrier 5 of room III. All the x-ray rooms had the ideal room size except facilities G and H. The design barrier thickness in the radiology department of all the conventional x-ray rooms involved in the study was adequate.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2022 Mohammed Sidi, Abubakar Aminu Abubakar, Anas Ya'u, Umar Mansur, Aliyu Abdullahi Hassan, Usman Tijjani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



