pH treatment on the optical and structural properties of niobium vanadium pentoxide nanoparticles for optoelectronics and energy storage applications
Keywords:
pH, Precipitation, Alkaline, Vanadium, NiobiumAbstract
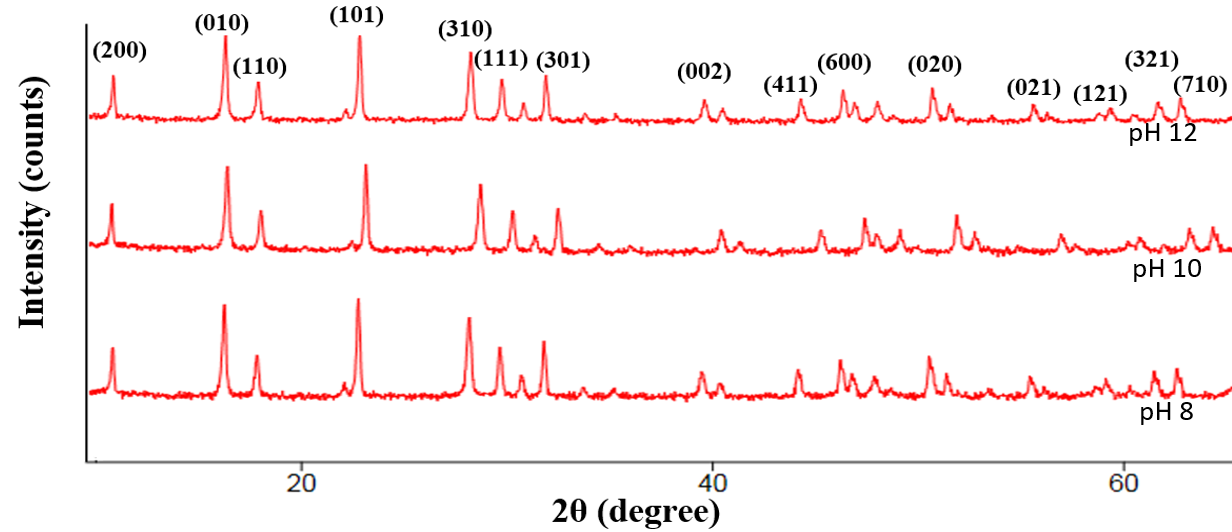
In this work, vanadium pentoxide is doped with niobium (Nb) particles using co-precipitation technique and effect of pH in alkaline medium was examined. The impact of pH on the optical, chemical, luminescence, morphological and structural characteristics of Niobium intercalated into vanadium pentoxide made by precipitation technique is disclosed. XRD technique was used to examine the structural properties such as interplanar spacing of the samples. The high interplanar spacing of 5.7835 Å obtained at pH 12 show that NbV2O5 sample can be used in energy storage device due to its large spacing. The energy band gap is decreased with increasing pH. The energy band gap for Nb-V2O5 samples generated at pH 8, 10, and 12 are 2.70, 2.50, and 2.30 eV. At approximately 680 nm, NbV2O5 nanoparticles revealed the emission of red light at all pH. One of the most important factors in improving the optical properties and crystallinity of nanostructured niobium doped vanadium oxide is lowering the pH level of the media. These nanostructures have great promise for the advancement of technological applications, particularly in the areas of UV filtering due to high absorbance revealed within the UV wavelength range. Niobium-doped Vanadium oxide nanoparticle is presently discovered as one of the storage device due to its large Interplanar spacing of 5.7835 Å at pH 12.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 A. A. Ibiyemi, J. I. Lawal, S. K. Aminu, A. G. Adewole, B. M. Akinroye, A. C. Adeniran, O. A. Abulude

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



