Electrochemical and Microstructural Characterization of Cr-Coated NdFeB in Neutral Wet Environment
Keywords:
Permanent magnet, Surface Coating, Cr–oxide, Corrosion protection, EISAbstract
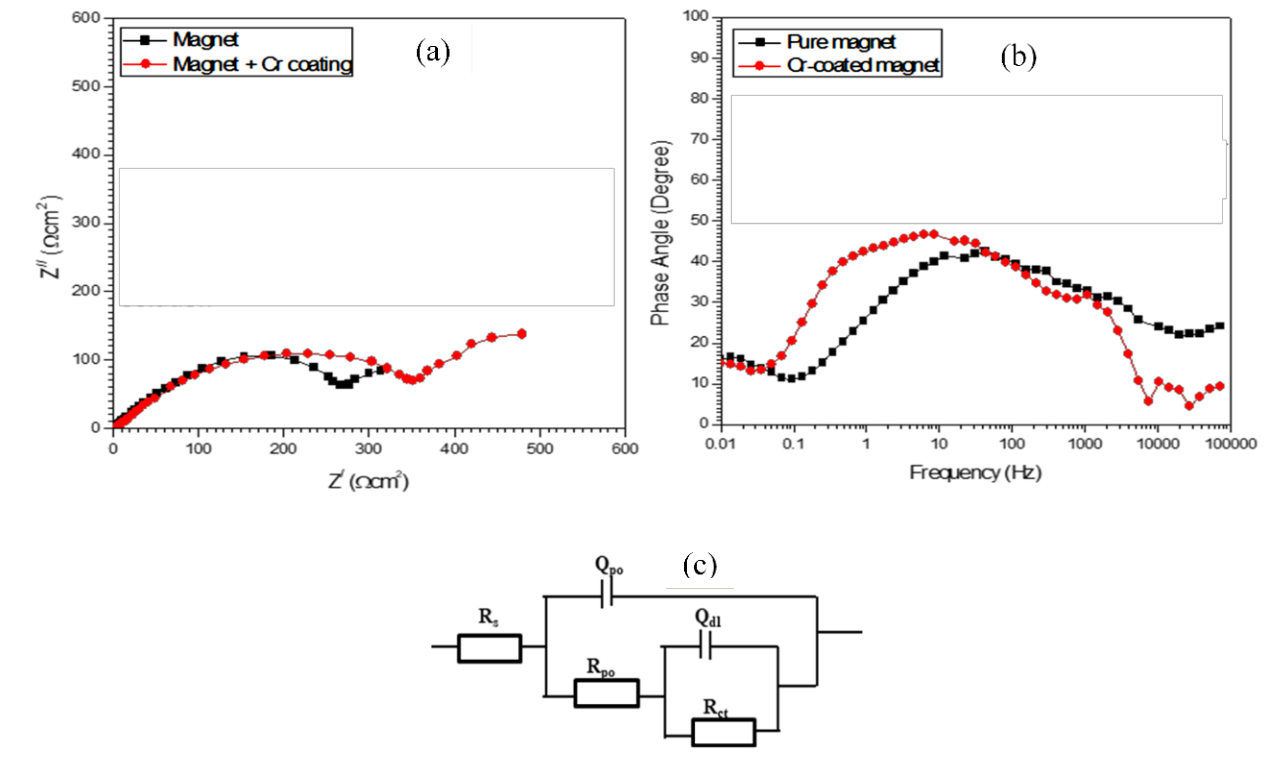
Naturally, NdFeB–based permanent magnets exhibit high chemical instability, especially, in wet environments. This makes them highly susceptible to corrosion, which leads to severe structural collapse. Applying thin surface coatings can improve the resistance to wet corrosion. In this work, 0.5 µm of chromium (Cr) film was sputtered on a sintered NdFeB–based magnet and the resistance to corrosion and microstructural damage was investigated in 3.5% NaCl solution with respect to an uncoated magnet. This was achieved by complementing potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy with scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The Cr coating caused a positive displacement of corrosion potential and lowered the rate of anodic dissolution. It also favored higher charge transfer resistance at the magnet–solution interface, and delivers a protection efficiency of ~ 60 %. Furthermore, grain boundary attack and deterioration were also significantly reduced by the Cr coating.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 V. Abanihi, K. K. Adama, I. B. Onyeachu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



