Physicochemical characteristics of soil and water in electronic waste dump site, Alaba Lagos, Nigeria
Keywords:
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), Congeners, Physicochemical characteristics, Soil, WaterAbstract
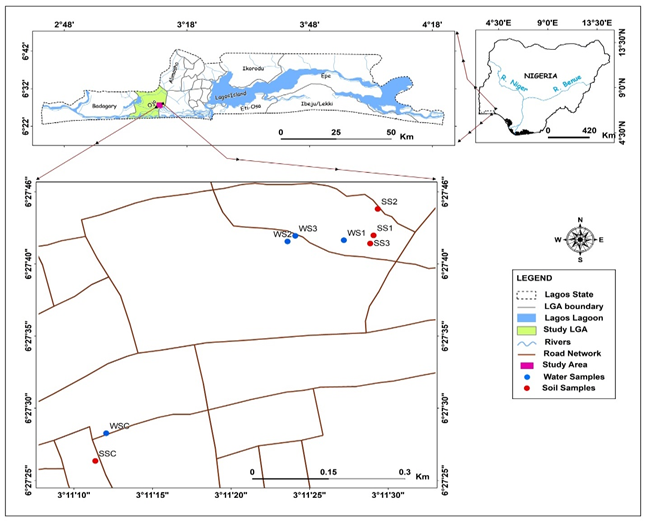
Determination of physicochemical characteristics of soil and water adjoining dumpsites is important to ascertain the fitness of drinkable water and their public health implications. Following the paucity of information on this area of study, physicochemical characteristics of water and soil in electronic waste dump site, Alaba, Lagos, Nigeria. Six samples from the dumpsite made up of three soil and water respectively were collected and extracted using USEPA methods. One soil and water sample far from the dumpsite served as control. Physicochemical parameters of water and soil samples were determined using standard methods. Results show that pH of the water samples ranged from 4.81 to 7.30. SW1 had highest pH (slightly alkaline) while SW3 had lowest pH and was acidic. The electrical conductivity of SW1, SW2 and SW3 ranged from 61 µS to 1421 µS respectively. Water temperature was between 29.53 and 29.57oC. Total dissolved solid of the water ranged from 32.33 to 722 mg/L. Sulphate ranged from 238 mg/L to 314 mg/L. Phosphate ranged from 41.92 to 60 mg/L. Dissolved oxygen ranged from 0.93 to 2.4 mg/L. Similarly, soil pH ranged from 6.57 to 7.44. Soil temperature ranged from 28.43 to 30.7. Soil organic carbon ranged from 13.75% to 20.25% while the soil organic matter ranged from 17.88% to 26.32%. Soil particle distribution ranged from 58.56 – 87.52% sand, 3.22 – 13.79% clay and 8.84 – 27.65% slit. Some physicochemical characteristics of soil and water in sampled location did not follow the WHO standard. This study has informed the state of water available for consumption as well as the state of soil contamination. Proper care is required to checkmate this location to avoid future contaminations.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 Emmanuel B. Oluwagbemi, Victor N. Enwemiwe, Ebenezer O. Ayoola, Clement C. Obi, John U. Okushemiya, Hilda Ufoegbune

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Ebenezer O. Ayoola, Victor N. Enwemiwe, Hilda O. Erhenhi, Clement C. Obi, Agboola A. Adebowale, Eric Esiwo, Joyce A. Onokpasa, Robert B. Ikomi, Acute toxicity of Oreochromis niloticus fingerlings exposed to effluent from Delta State University, Abraka Nigeria boys hostel , African Scientific Reports: Volume 3, Issue 2, August 2024



