A Simulation Study on Robustness of One Sample Inferential Statistics in Mixture Distribution
Keywords:
Inferential statistics, Mixture distribution, Non-normality, Simulation studyAbstract
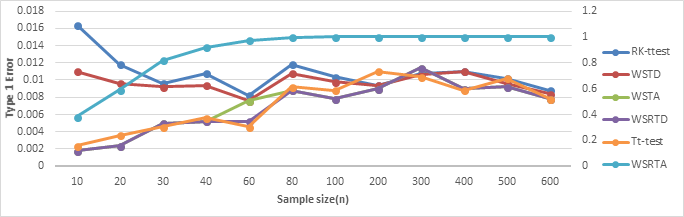
Mixture distribution refers to the combination of more than one probability distribution. Meanwhile, non-normality of data set may be inevitable and the cause may be as a result of mixed distributions thereby renders parametric tests ineffective. Montecarlo experiment was performed 5000 times under twelve sample sizes where data were generated from Gaussian and Cauchy distributions using R-statistical packages. At three commonly used alpha levels (0.1, 0.05 and 0.01), the robustness of the test statistics (Rank transformation t-test, Wilcoxon sign test (Distribution and Asymptotic), Signed rank test (Distribution and Asymptotic) and Trimmed t-test) were examined. When the type I error rate of a statistic approximately equal to the true error rate then the statistic is considered robust. At 0.1 and 0.05, Rank transformation t-test, Wilcoxon sign test (distribution) and Trimmed t-test in this order are robust. Meanwhile, at 0.01 Rank transformation andWilcoxon sign test (distribution) were identified to be robust. Also, further counts at all levels of significance revealed that the Rank transformation test is robust and thereby recommended when data comes from a mixed distribution. Hence, this study has been able to identify test statistics that are robust when data comes from a mixed distribution in one sample problem.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2022 T. J. Adejumo, A. A. Akomolafe, A. I. Okegbade, S. D. Gbolagade

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Taiwo J. Adejumo, Kayode Ayinde, Abayomi A. Akomolafe, Olusola S. Makinde, Adegoke S. Ajiboye, Robust-M new two-parameter estimator for linear regression models: Simulations and applications , African Scientific Reports: Volume 2, Issue 3, December 2023



