ECG anomaly detection: a deep learning perspective with LSTM encoders
Keywords:
Anomaly, Anomaly detection, LSTM, Autoencoder, Electrocardiogram, Deep learningAbstract
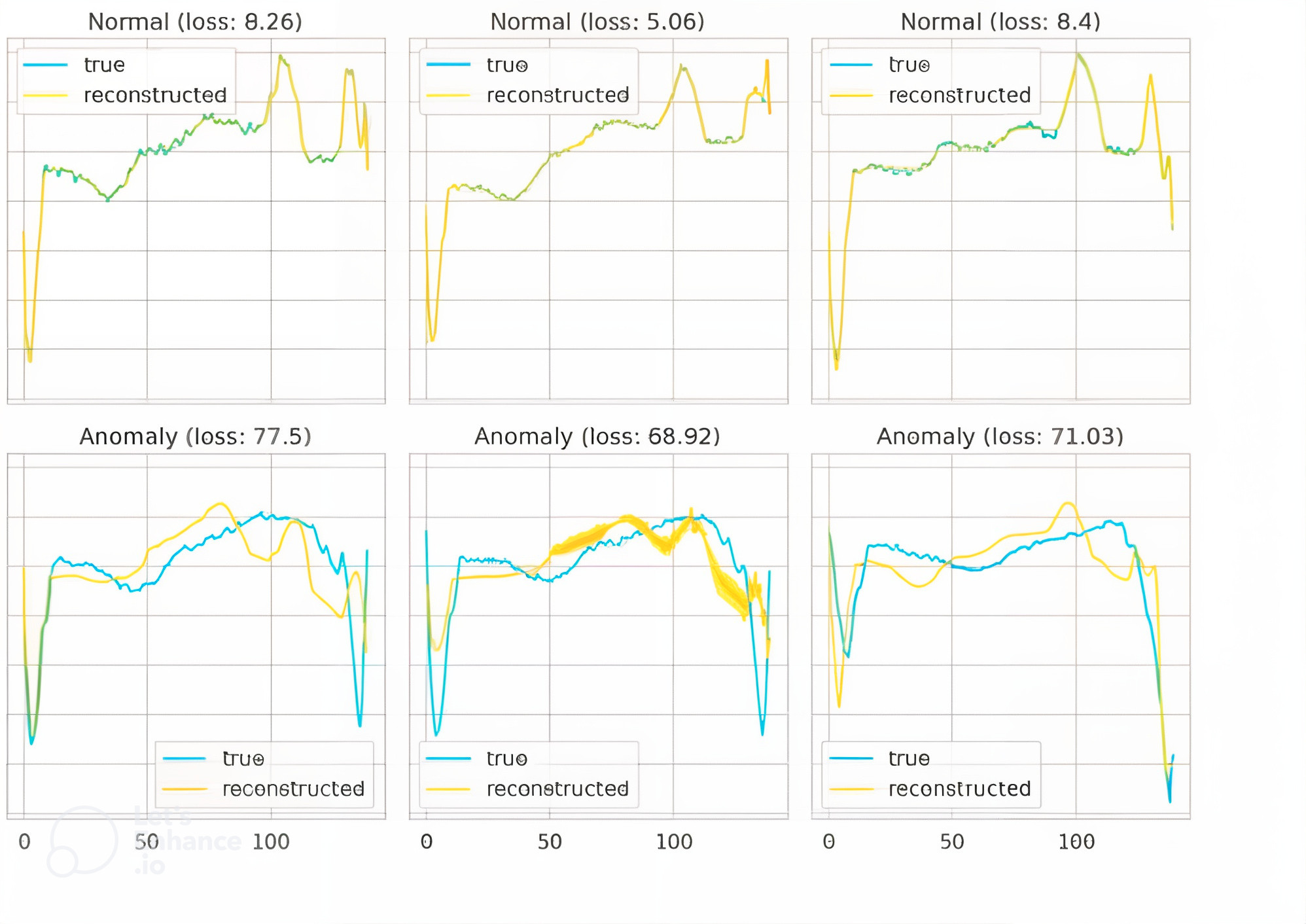
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a procedure that measures the heart’s electrical activity. Each heartbeat generates an electrical impulse, causing the heart muscle to contract and pump blood. ECG data is a classic example of time series data, where the timing of the upper and lower chambers of the heart is analyzed by medical professionals. The use of unsupervised learning techniques, such as K-Means Clustering and Hierarchical Temporal Memory (HTM) to ECG anomaly detection often results in poor performance due to their dependability on pre-defined features. The performance of a multilayer convolutional neural network adapted to the unsupervised task is also constrained by lack of quality feature extraction and guidance from labelled data. This research proposes a deep learning approach using Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) Networks for the ECG signal analysis to improve the accuracy of anomaly detection in heartbeats. The proposed method was evaluated on the ECG5000 dataset. The model achieved an impressive accuracy of 99.23%, Specificity of 99.25% and Area under curve (AUC) of 98.00%, thereby outperforming existing models. The results demonstrate that the LSTM Autoencoder-based approach effectively learns expressive representations of ECG sequences, leading to improved performance compared to previous methods.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Adenike Adegoke-Elijah, Theresa Omolayo Ojewumi, Kudirat Oyewumi Jimoh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



