Measurement and simulation of indoor radon concentration distribution in students’ residential hostels around Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Ogbomoso, Nigeria
Keywords:
Indoor radon, Air change rate, Annual absorbed dose, Annual effective dose, Radon monitoringAbstract
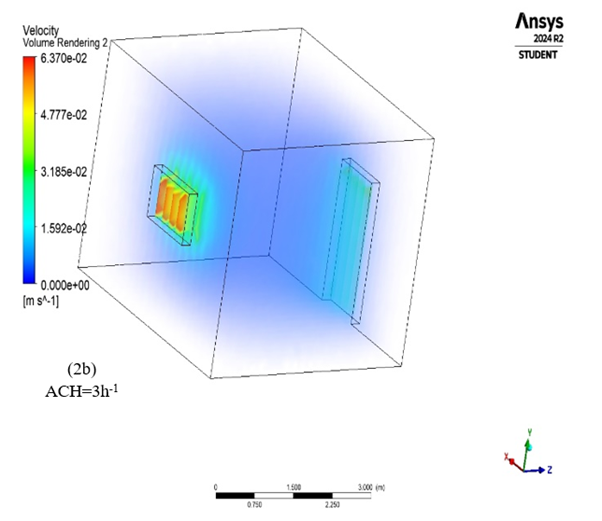
Radon is a harmful gas and class I carcinogen posing global challenge to human health. Being an inert gas, it is impossible to perceive its presence by any of the sense organs, thus the application of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation in radon study is enhancing human understanding of the behavior and distribution of radon in indoor air. Hence, this work measured the indoor radon concentration (Ri) in student’s residential hostels and evaluate radon gas distribution in indoor air. In-situ measurement of the Ri in 10 student’s residential hostels was carried for a period of one month using RAD7. The CFD code ANSYS Fluent 2024R2, based on the finite volume method was employed in modeling the geometry of the student’s room, calculate, predict and visualize the concentration and distribution of radon inside the room. The average measured Ri was 45.89 Bq/m3 with a corresponding annual effective dose of 1.042 mSv/yr. The simulation revealed an average value of 45.51 Bq/m3 and the annual effective dose from the inhalation of radon when ACH is 2, 3 and 4 h-1 respectively was calculated to be 1.03 mSv/yr, which is lower than the recommended value by ICRP. The simulation revealed that radon gas is more concentrated at the building window compare to other parts of the building. It is therefore recommended that the indoor radon induced air be diffused with external or fresh air by ensuring adequate ventilation and maintaining healthy air circulation.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 E. A. Oni, C. O. Ajiboye, P. S. Ayanlola, O. O. Oloyede, A. A. Aremu, T. A. Olajide, O. O. Oladapo, O. P. Oyero, A. E. Oladipo, M. K. Lawal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



