Optimal distribution of vehicular traffic flow with Dijkstra’s algorithm and Markov chains
Keywords:
Dijkstra’s algorithm, Markov chains, Vehicular traffic flow, Traffic optimizationAbstract
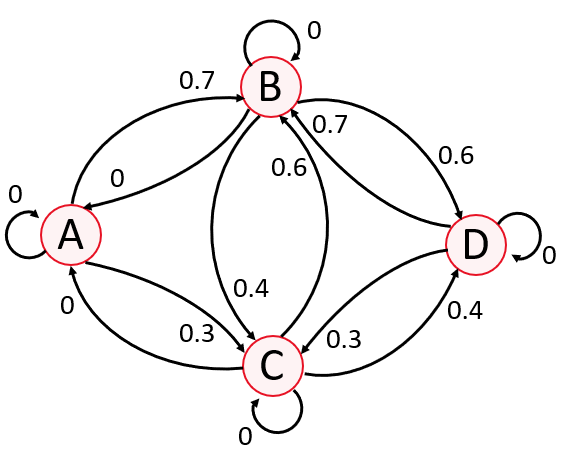
The optimization of traffic distribution is a critical problem in transportation networks, where efficient routing can reduce congestion, minimize travel time, and improve overall traffic flow. This work explores the combined application of Dijkstra’s algorithm and Markov chains to model and optimize vehicular traffic distribution in road networks linking multiple cities. Dijkstra’s algorithm is deployed to determine the shortest path between two nodes in a weighted graph, allowing for optimal, real-time routing of vehicles across a network based on minimal distance or congestion. In parallel, Markov chains are used to model the long-term probabilistic distribution of traffic across various routes, providing insights into steady-state traffic flows and congestion patterns. The combination of these two approaches addresses both immediate and long-term traffic management concerns. Our findings show that while Dijkstra’s algorithm offers immediate routing solutions, Markov chains can model the long-term behavior of traffic, leading to a more efficient planning and decision-making.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 L. I. Igbinosun, N. R. Udoenoh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



