Synthesis and characterization of ZnO crystalline powder: effect on Alkaline pH
Keywords:
Optoelectronics, pH, Transmittance, Absorbance, ZnOAbstract
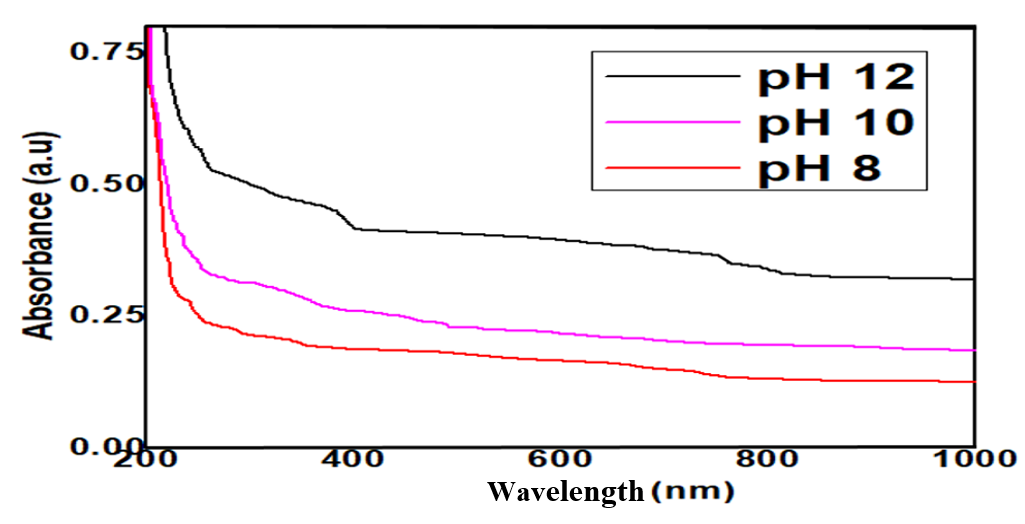
Zinc Oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) were effectively produced using the co-precipitation method in alkaline solutions with pH values of 8, 10, and 12. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) investigation indicates that the preferred orientation for the formation of ZnO phase and wurtzite-hexagonal structure is the (101) reflection plane. The crystallite size of ZnO produced at pH 8, 10, and 12 are 29.74, 17.83, and 12.64 nm, respectively. The scanning electron microscope (SEM) result revealed spongy-like morphology and spherical grains nanostructure at all pH level. XRD analysis demonstrated that the hexagonal wurtzite structure is present in the ZnO nanostructure. The energy band gap is decreased with increasing pH. The smooth and uniform shape of sample synthesized at pH 12 with large-scale homogeneity is an important point, this suggests that these nanoparticles may be useful for photodetectors. Because of its high optical gain, the ZnO NPs synthesized at pH 8 exhibits the best optical characteristics, whereas the ZnO NPs created at pH 12 exhibits optical losses for optoelectronics device application. This work has shown that altering the precursor’s pH altered the zinc oxide sample for a range of industrial uses. For example, using pH 12 greatly raised the absorbance value, showing that ZnO is a promising photovoltaic (PV) material and ultraviolet (UV) detector since its light absorption is much boosted at high pH values. Meanwhile, the addition pH 8 greatly raised the transmittance value, demonstrating that ZnO’s visible light transparency is significantly enhanced at low pH levels in alkaline medium, making it a potential optoelectronics material and active infrared detector. According to the study’s findings, ZnO NPs has use in photovoltaic materials, optoelectronics, and UV and infrared detectors.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 A. A. Ibiyemi, B. M. Akinroye, O. P. Oladipo, I. E. Olaoye, M. T. Olatunji, T. I. Ogunniran, A. T. Oladimeji, A. O. Ogungbe, A. S. Olatunde, G. O. Ogunyemi, S. K. Aminu, A. F. Ojo, A. Adewole, J. I. Lawal, A. C. Adeniran

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



