Bayesian analysis of the effects of some identified risk factors of systolic pressure among pregnant women in Ogbomoso, Oyo State
Keywords:
Bayesian logit, Prior, clinical- genetic risk factorsAbstract
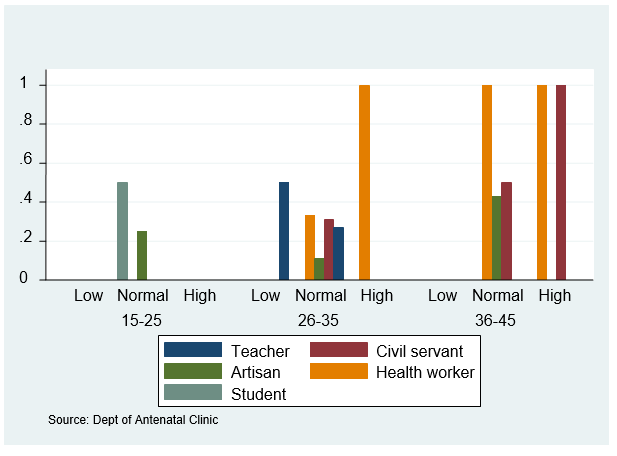
Unhealthy condition during pregnancy is a function of abnormal Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP). Therefore, this becomes a threat to women and health policy makers on how to reduce the consequence of high SBP. To overcome this challenge, appropriate model must be specified to capture some identified clinical-genetic factors for SBP in pregnant women when the informative prior to these factors is not sufficiently available. The aim of the study is to develop a Bayesian Logit (BLM) to calculate probabilities of different SBP outcomes among pregnant women in LAUTECH Teaching Hospital, Oyo State. The results shows that age, packed cell volume and genotype increase the likelihood of having High Systolic Blood Pressure (HSBP), while blood group and occupation increase the likelihood of having low Systolic Blood Pressure (LSBP) among pregnant women. Also, the probabilities of increase in height and weight cause a systematic change in the SBP among pregnant women. The study concludes that the identified clinical and genetic risk factors contribute to the likelihood of having HSBP and LSBP among pregnant women in Ogbomoso, Oyo State.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 A. P. Onatunji, O. M. Ajao, K. T. Amzat, L. A. Oladimeji, O. A. Olalude

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



