Deploying persuasive technology-based model in the prevention and control of malaria in Nigeria to reduce incidence of deaths
Keywords:
Persuasive technology, Malaria prevention and control support system (MPCSS), Active intervention tool, Mosquitoes, Malaria related deaths (MRDs)Abstract
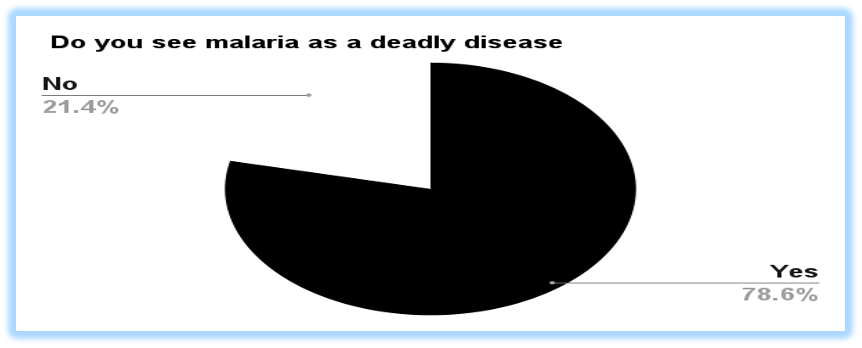
Specifically among pregnant women and young children under the age of five, malaria is one of the major causes of illnesses and fatalities in Nigeria, and in Africa in general. According to recent research, malaria-related deaths (MRDs) have risen even though the government has implemented numerous intervention strategies to combat this deadly among Nigerians. This is a result of people not using such intervention methods to protect themselves. Further research into why people don’t comply with intervention systems effectively revealed that the interventions are passive, and sometimes complicated to adopt. Consequently, we established three quantifiable research outcomes that will allow us to assess if persuasive technology is appropriate for eradicating malaria-related deaths. We utilize participatory system design (PSD) and User-Centered methods to collect data from research. The participants provided answers to well-designed questionnaires that were used to gather information to analyze the impact of persuasive technology on the prevention and control of malaria-related deaths. The modeling of the intervention system uses the information gathered from the research survey. The Malaria Prevention and Control Support System (MPCSS), an intervention system, was developed and deployed as part of the research in three phases, and its effectiveness was assessed by an evaluation study. The study revealed that applying the suggested persuading technology-based methodology boosted ownership of mosquito nets, involvement in malaria prevention and control activities, and understanding of the risk of malaria-related mortality.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 Ignatius Nwoyibe Ogbaga, Henry Friday Nweke, Juliana Ngozi Ndunagu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Ignatius Nwoyibe Ogbaga, Henry Friday Nweke, Persuasive power of artificial intelligence-generated ads: exploring online behaviour among Gen Z internet users in Nigeria , African Scientific Reports: Volume 4, Issue 3, December 2025



